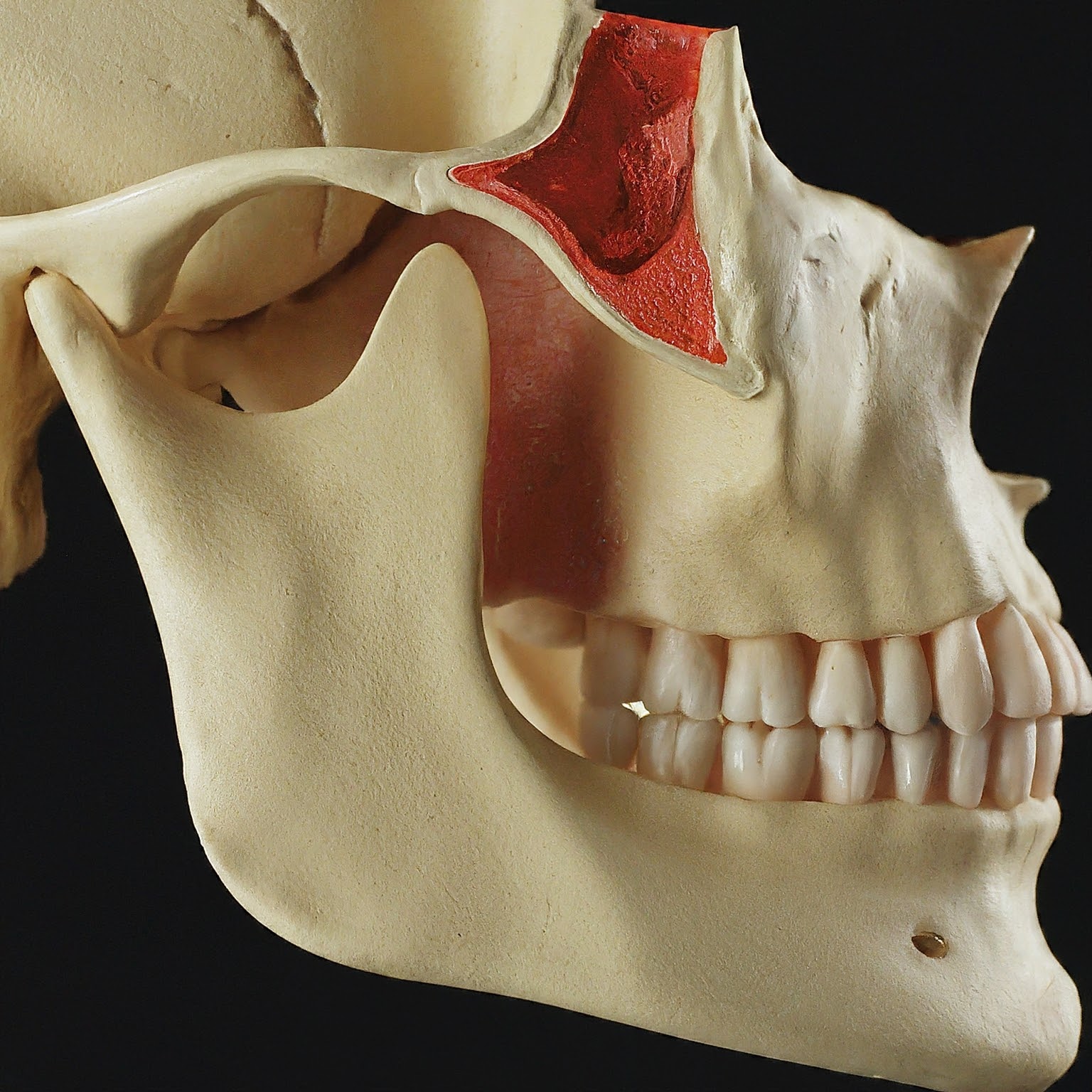
What is TMJ?
TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint, a crucial part of your anatomy that connects your jawbone (mandible) to your skull, located just in front of your ears on both sides of your head. This joint is responsible for a wide range of jaw movements, including opening and closing your mouth, chewing, speaking, and yawning. The TMJ is unique because it functions as both a hinge and a sliding joint, allowing for the complex range of motions needed for everyday activities.
What Are TMJ Disorders?
TMJ disorders (TMD) refer to a group of conditions that affect the temporomandibular joint and the surrounding muscles and tissues. These disorders can cause significant discomfort and dysfunction, impacting your ability to perform simple tasks like eating and speaking.
Common Causes of TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders can arise from various factors, and sometimes, the exact cause remains unclear. Here are some of the most common contributors:
- Jaw Injury or Trauma: An injury to the jaw, head, or neck can disrupt the alignment of the TMJ, leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Arthritis: Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the TMJ, causing inflammation and deterioration of the joint.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Chronic teeth grinding or clenching, often occurring during sleep, can place excessive strain on the TMJ and surrounding muscles, leading to pain and damage.
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to muscle tension in the jaw and neck, which may contribute to the development of TMJ disorders.
- Misalignment of Teeth or Jaw: Improper alignment of the teeth or jaw, often due to orthodontic issues, can strain the TMJ over time.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing TMJ disorders due to genetic factors that affect joint structure or function.
Symptoms of TMJ Disorders
The symptoms of TMJ disorders can vary widely, but some of the most common ones include:
- Jaw Pain or Tenderness: Pain that can be felt in the jaw, face, neck, or shoulders.
- Headaches: Often resembling tension headaches, particularly around the temples.
- Ear Pain or Pressure: Discomfort or a feeling of fullness in the ears, sometimes accompanied by ringing (tinnitus).
- Difficulty Chewing: Pain or discomfort while eating, especially when chewing tough or sticky foods.
- Jaw Locking: The jaw may lock in an open or closed position, making it difficult to move.
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: Noises in the jaw joint when opening or closing the mouth, sometimes accompanied by pain.
Diagnosing TMJ Disorders
If you suspect you have a TMJ disorder, it’s essential to seek a professional diagnosis. A dentist, oral surgeon, or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may evaluate your condition through:
- Physical Examination: Assessing jaw movement, tenderness, and listening for clicking or popping sounds.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to get a detailed view of the joint, surrounding bones, and soft tissues.
- Dental Examination: Checking for signs of teeth grinding, malocclusion (improper bite), or other dental issues.
Treatment Options for TMJ Disorders
Treatment for TMJ disorders varies depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment approaches:
1. Self-Care and Lifestyle Changes
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can alleviate muscle tension in the jaw.
- Dietary Adjustments: Eating soft foods and avoiding chewing gum can reduce strain on the jaw.
- Jaw Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve jaw mobility and reduce symptoms.
2. Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage mild pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: Prescribed for short-term use to reduce muscle tension.
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce inflammation and pain.
3. Dental Treatments
- Mouth Guards or Splints: Custom-fitted devices worn over the teeth can prevent teeth grinding and alleviate pressure on the TMJ.
- Orthodontic Treatment: In cases where misaligned teeth contribute to TMJ disorders, orthodontic treatment may be necessary to correct the alignment.
4. Physical Therapy
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like massage or myofascial release can reduce muscle tension and improve jaw function.
- Ultrasound or Electrical Stimulation: These modalities can help reduce pain and inflammation.
5. Invasive Procedures
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the joint can reduce inflammation in severe cases.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the temporomandibular joint.
Preventing TMJ Disorders
While not all TMJ disorders can be prevented, taking proactive steps can reduce your risk:
- Practice Good Posture: Avoid slouching, especially when sitting for extended periods, to reduce strain on the neck and jaw.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-relief techniques into your daily routine to prevent muscle tension.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Limit the consumption of hard, chewy, or sticky foods that can strain the jaw.
Conclusion
TMJ disorders can significantly impact your quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, many people find relief from their symptoms. If you’re experiencing jaw pain, discomfort, or other symptoms related to TMJ, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options for your condition.
This blog post provides an overview of TMJ, its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options, making it informative for readers seeking to understand or manage TMJ disorders.