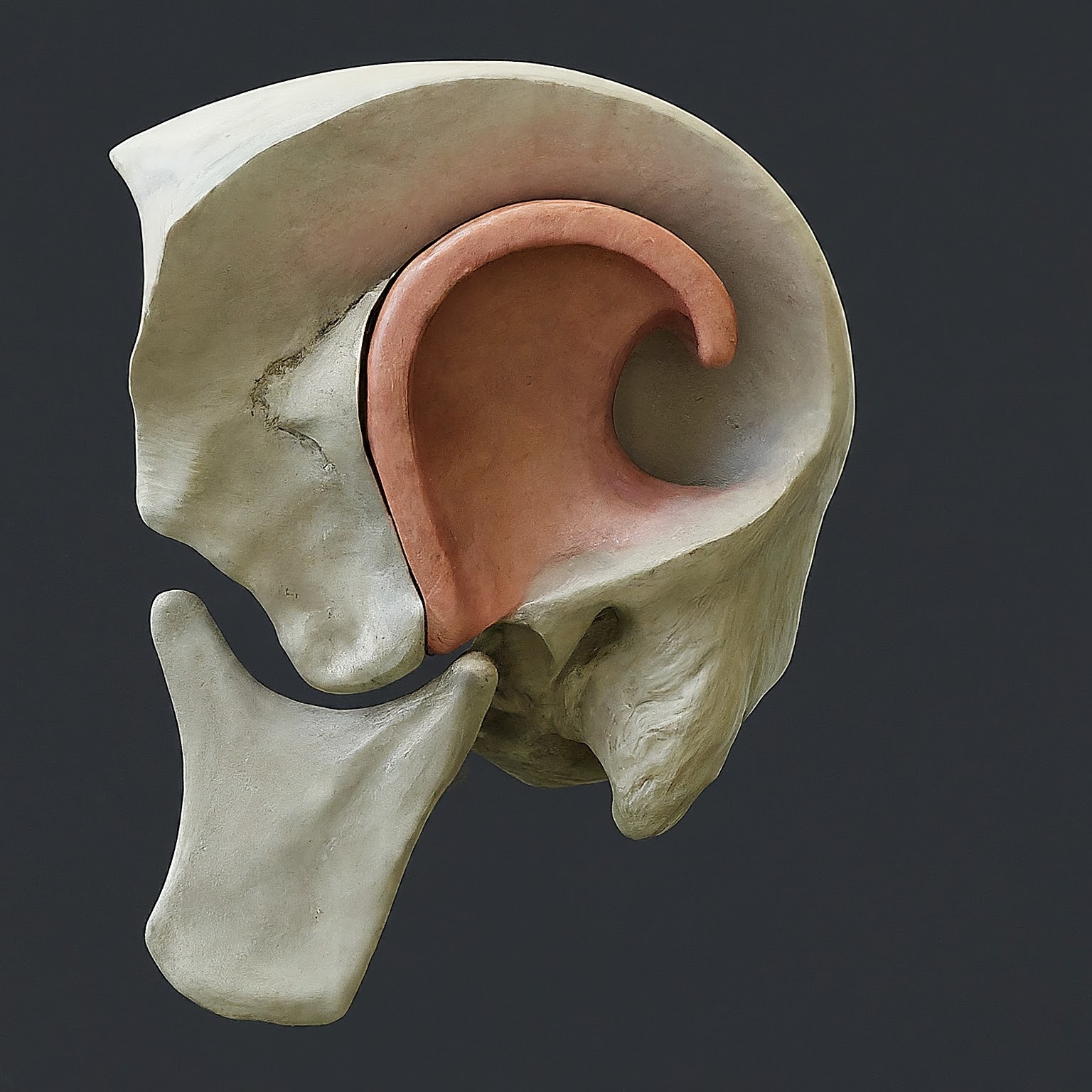
The temporal bone is a crucial part of the skull, located on the sides and base of your head, just above the ears. It plays several important roles in protecting vital structures and supporting key functions in the body.
What is the Temporal Bone?
The temporal bone is a paired bone, meaning there’s one on each side of the skull. It consists of four parts: the squamous, tympanic, mastoid, and petrous parts. Each of these parts has specific functions:
- Squamous Part: The flat, fan-shaped portion of the bone, which forms the side of the skull.
- Tympanic Part: This part surrounds the external auditory canal, playing a key role in hearing.
- Mastoid Part: Located behind the ear, it contains air cells that help regulate ear pressure and protect the ear structures.
- Petrous Part: The hardest part of the temporal bone, housing the inner ear structures essential for hearing and balance.
Functions of the Temporal Bone
The temporal bone serves several vital functions:
- Protection: It safeguards the delicate structures of the inner ear, including the cochlea and vestibular system, which are essential for hearing and balance.
- Hearing: The temporal bone surrounds and supports the auditory canal and middle ear structures, playing a critical role in the process of hearing.
- Muscle Attachment: Several muscles, including those involved in chewing and moving the head, attach to the temporal bone.
- Facial Nerve Passage: The facial nerve, which controls facial expressions, passes through the temporal bone.
Common Issues Related to the Temporal Bone
Problems with the temporal bone can lead to a variety of symptoms and conditions, including:
- Temporal Bone Fractures: Usually caused by trauma, fractures can affect hearing, balance, and facial movement.
- Mastoiditis: An infection of the mastoid part of the temporal bone, often resulting from untreated ear infections.
- Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMD): The temporal bone forms part of the TMJ, and issues here can lead to jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty chewing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms like persistent ear pain, hearing loss, dizziness, or facial nerve issues, it’s important to seek medical advice. These could be signs of a problem with the temporal bone that may require treatment.
The temporal bone may not be something you think about daily, but its role in protecting your senses and supporting essential functions makes it a cornerstone of your cranial anatomy. Understanding its importance can help you appreciate the intricate design of your body and the need to care for it.